Search Market Research Report
Ocean Energy Market Size, Share Global Analysis Report, 2025 - 2034
Ocean Energy Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis Report By Type (Wave Energy, Tidal Energy, and Others), By Application (Residential, Commercial), And By Region - Global Industry Insights, Overview, Comprehensive Analysis, Trends, Statistical Research, Market Intelligence, Historical Data and Forecast 2025 - 2034
Industry Insights
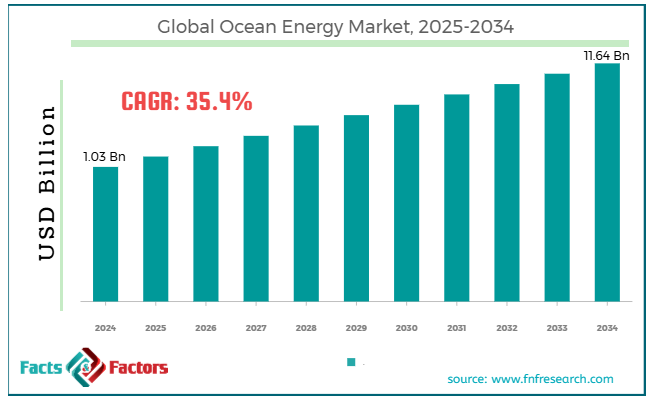
[221+ Pages Report] According to Facts & Factors, the global ocean energy market size was worth around USD 1.03 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 11.64 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 35.4% between 2025 and 2034.
 Market Overview
Market Overview
Ocean energy is the energy utilized from the properties and natural movements of the ocean. It is captured in diverse forms, comprising wave energy, tidal energy, salinity gradient energy, and ocean thermal energy. These technologies are still progressing, but hold significant potential as renewable power sources due to the constant and vast nature of ocean movements. The worldwide ocean energy market is projected to experience momentous growth in the coming years due to increasing renewable energy demand, technological improvements, and climate change mitigation.
With the global pressure towards decarbonizing power sectors, the demand for cleaner, renewable energy sources is also rising. Ocean energy is abundant and predictable, making it an ideal fit for this strategy and thus propelling the industry's growth. The development of more cost-efficient and effective ocean energy solutions, like improved energy capture systems, enhanced materials, and better turbines, is supporting the progress of the global market. Ocean energy also offers a better way to alleviate climate change by decreasing dependency on fossil fuels. This ecological benefit drives companies and governments to invest heavily in ocean energy as a key component of clean energy solutions.
However, the global market is anticipated to face barriers like technological challenges and stresses regarding ecological impact. Although the global market is advancing with key growth drivers, several ocean energy solutions are still in experimental or early commercial phases. Concerns like durability, efficiency, and maintenance in extreme environments remain key technological obstacles.
Moreover, since ocean energy is regarded as a clean source, tensions related to its potential ecological effects include the disturbances of ecosystems and marine life, variations in water flow patterns, and noise pollution. Yet, the global market will grow substantially over the estimated period owing to the emergence of better energy storage solutions and increasing international collaborations in research.
Incorporating ocean energy with energy storage solutions like hydrogen or batteries can help alleviate intermittency problems and offer more consistent energy generation, thus fueling market sustainability. In addition, with the evolution of ocean energy solutions, there is a key opportunity for universal collaboration in R&D and the sharing of suitable practices. This global cooperation may significantly reduce costs and boost innovations.
 Key Insights:
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global ocean energy market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 35.4% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global ocean energy market size was valued at around USD 1.03 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 11.64 billion by 2034.
- The ocean energy market is projected to grow significantly owing to the rising demand for renewable energy, the development of cost-effective and efficient ocean energy solutions, and climate change mitigation.
- Based on product, the tidal energy segment is expected to lead the market, while the wave energy segment is expected to grow considerably.
- Based on application, the commercial segment is the dominating segment, while the residential segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
 Growth Drivers
Growth Drivers
- Diversification and energy security drive the ocean energy market growth
Ocean energy offers a route to better energy security. The accessibility of ocean resources in most parts of the world increases their significance as an essential resource for nations that aim to diversify their power supply and decrease reliance on imported fuels.
Tidal power and offshore wind can offer reliable baseload energy, with predictions suggesting that tidal power may meet nearly 20% of the power demands for some economies, like the United States and the United Kingdom, by 2050.
The Gulf of Mexico (U.S.) is presently a new region of focus for offshore wind power. Hecate Energy, a leading power company, is adopting plans to launch 133 offshore turbines in the area. This will contribute to both local economic growth and energy security.
Nations like Australia and Japan aim to offshore wave energy to expand their power sources, mainly in island or remote communities, where conventional energy is vulnerable and expensive.
- How will surging global investments in clean technology considerably fuel the ocean energy market growth?
The rise in investments in clean technology is a leading driver of the global ocean energy market. The ocean energy subdivision attracts significant capital from governmental bodies and private investors. The growing emphasis on clean and sustainable technologies fuels modernization and drives the market toward commercialization.
A prominent renewable energy company, Ørsted, is among the key players capitalizing on ocean energy, mainly wave technologies and offshore solutions. Nonetheless, it has experienced key challenges since its stock price dropped because of broad market fluctuations and management concerns. This caused issues regarding its ability to fund impending ocean energy projects. The World Bank is also fueling investments in such projects in emerging economies, mainly in Pacific islands and Southeast Asia, where the availability of affordable and clean energy is essential for economic development.
 Restraints
Restraints
- Growing competition from other renewables constraints the progress of the ocean energy market
Ocean Energy experiences heated competition from many other highly established renewable power technologies like solar, wind, and hydropower, which are more scalable, cheaper, and easier to deploy. Since these substitutes are growing more common and cost-effective, Ocean Energy struggles to compete for industry share and funding.
According to the IRENA Renewable Energy Cost Database, offshore wind and solar technologies have experienced cost reductions of over 80% in the past decade, thereby increasing their prominence as investment options compared to ocean energy.
Tesla Energy announced the expansion of battery storage and solar solutions, which, when combined with inexpensive onshore wind, have significantly outperformed in terms of deployment speed and cost.
 Opportunities
Opportunities
- Will the social and environmental advantages of ocean energy drive market growth?
Ocean energy provides numerous ecological benefits that comply with worldwide sustainability goals. The opportunity to decrease greenhouse gas emissions and create new marine employment and environmental businesses is a focus for policymakers, primarily recognizing climate change mitigation.
As per IRENA, Ocean Energy holds the potential to supply 10% of the global power by 2040, which may result in a drop of 5 gigatons of carbon dioxide yearly.
The (NOAA) National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration mentioned that the United States East Coast may generate 5 gigawatts of tidal power by 2030, thus aiding the nation in achieving its carbon reduction objectives and providing fresh job opportunities in the marine energy industry.
 Challenges
Challenges
- Do licensing and regulatory concerns limit the growth of the ocean energy market?
The regulatory outlook for ocean energy projects is challenging and differs by region. The licensing procedure for these projects may be slow, with several nations lacking exhaustive and clear guidelines on accepting or handling these projects. These regulatory delays may extend the time-to-market for novel technologies, thus hampering growth and negatively affecting the ocean energy industry.
In the U.S., the BOEM, or Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, which supervises offshore renewable energy projects, has been criticized for the time it takes to issue approval for novel energy projects. A review in 2024 found that some wave and tidal energy projects were waiting for acceptance for more than 7 years.
The U.S. Senate presented a bill in April 2024 to simplify the regulatory process for offshore renewable energy, including wave and tidal energy. Nonetheless, the bill is still being debated and has not yet been approved.
 Report Scope
Report Scope
Report Attribute |
Details |
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 1.03 Billion |
Projected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 11.64 Billion |
CAGR Growth Rate |
35.4% CAGR |
Base Year |
2024 |
Forecast Years |
2025-2034 |
Key Market Players |
Siemens Gamesa, Verdant Power, Ocean Infinity, Minesto, OpenHydro, Atlantis Resources, Oceans of Energy, Magallanes Renovables, Principle Power, Aquatera, CorPower Ocean, Schottel Hydro, Marine Power Systems, Tidal Lagoon Power, SIMEC Atlantis Energy, and others. |
Key Segment |
By Product, By Application, and Region |
Major Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East &, Africa |
Purchase Options |
Request customized purchase options to meet your research needs. Explore purchase options |
 Segmentation Analysis
Segmentation Analysis
The global ocean energy market is segmented based on product, application, and region.
Based on product, the global ocean energy industry is divided into wave energy, tidal energy, and others. The tidal energy segment registered a substantial market share in 2024 and will continue to dominate. This growth is backed by its higher energy predictability, improved technological development, and robust industry momentum concerning installed capacity. Tidal energy technology, especially tidal stream turbines, is more highly developed than wave energy. Multiple tidal projects have already gained commercial development, while most others are still in their demonstration stages for wave energy. Tidal energy benefits from the predictability of tides, allowing for more reliable energy generation than the intermittent property of wave energy.
Based on application, the global ocean energy industry is segmented into residential and commercial. In 2024, the commercial segment registered notable growth, with promising developments in the future as well. This segmental growth is backed by commercial power generation, large-scale projects, and the rising need for grid stability in island and coastal areas. Ocean energy solutions like wave energy and tidal energy are still expensive for maintenance and deployment, which increases their suitability for commercial-scale projects instead of just residential installations.
Moreover, ocean energy projects are likely to involve long-term PPAs (power purchase agreements) with large businesses and government organizations, increasing their financial practicality to produce energy abundantly for industrial and commercial consumers. Also, several islands and coastal regions that face challenges in energy access or are off-grid use wave and tidal energy as a clean energy source to enhance energy security and decrease reliance on fossil fuels.
 Regional Analysis
Regional Analysis
- What factors will help North America dominate the ocean energy market over the forecast period?
North America held a leading position in the global ocean energy market in 2024 and is expected to continue dominating in the future. This remarkable growth is attributed to innovations and early adoption of modern technologies, rich coastal resources, and growing private sector investment. North America, especially Canada and the United States, has been a forerunner in commercializing and developing ocean energy technologies, mainly wave and tidal energy. It is home to a few of the world's advanced research centers, universities, and private organizations that emphasize ocean energy innovations. North America is also strategically situated in regions with the most predictable and abundant ocean energy resources, mainly along the coasts of Canada and the United States.
Furthermore, the region's private sector has contributed to driving ocean energy development, with startups and large businesses investing in modern technological projects. This investment is crucial for commercializing ocean energy solutions, particularly in the face of significant initial capital costs.
Europe is projected to progress as the second-leading region in the ocean energy market, owing to government support, abundant natural resources, and technological improvements and leadership. Europe holds one of the most supportive policy and regulatory environments for ocean energy development, with strong backing within its nations and at the European Union level. The region benefits from highly favorable natural conditions for ocean energy, comprising high wave energy potential, substantial tidal ranges, and vast coastal areas.
Europe's geography offers access to a few of the most potent and consistent tidal and wave energy resources on a global scale. The region also leads in developing ocean energy technologies, with a broader range of well-developed research institutions and companies fueling wave and tidal energy modernization. The region is also home to several developers of improved ocean energy and holds a promising marine renewable energy sector.
 Competitive Analysis
Competitive Analysis
The global ocean energy market is led by players like:
- Siemens Gamesa
- Verdant Power
- Ocean Infinity
- Minesto
- OpenHydro
- Atlantis Resources
- Oceans of Energy
- Magallanes Renovables
- Principle Power
- Aquatera
- CorPower Ocean
- Schottel Hydro
- Marine Power Systems
- Tidal Lagoon Power
- SIMEC Atlantis Energy
 Key Market Trends
Key Market Trends
- Growing trend of hybrid energy systems:
Incorporating ocean energy with offshore wind and various renewable energy sources is becoming increasingly popular. Hybrid systems are being developed to enhance energy output, optimize grid stability, and reduce costs. Nations like Scotland are the forerunners in the development of blue energy technologies.
- Demonstration farms and pilot projects:
There has been a growth in demonstration farms on a global scale and pilot projects, especially in Canada, the United Kingdom, and Portugal, to examine the commercial feasibility of ocean energy solutions. These projects are vital for augmenting ocean energy and attesting its capabilities to the global and national renewable energy objectives.
The global ocean energy market is segmented as follows:
 By Product Segment Analysis
By Product Segment Analysis
- Wave Energy
- Tidal Energy
- Others
 By Application Segment Analysis
By Application Segment Analysis
- Residential
- Commercial
 By Regional Segment Analysis
By Regional Segment Analysis
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- The Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Egypt
- Kuwait
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Industry Major Market Players
- Siemens Gamesa
- Verdant Power
- Ocean Infinity
- Minesto
- OpenHydro
- Atlantis Resources
- Oceans of Energy
- Magallanes Renovables
- Principle Power
- Aquatera
- CorPower Ocean
- Schottel Hydro
- Marine Power Systems
- Tidal Lagoon Power
- SIMEC Atlantis Energy
Frequently Asked Questions

Copyright © 2025 - 2026, All Rights Reserved, Facts and Factors


