Search Market Research Report
Landfill Gas to Energy (LFGTE) Systems Market Size, Share Global Analysis Report, 2025 - 2034
Landfill Gas to Energy (LFGTE) Systems Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis Report By Capacity (Small Scale [Below 500 kW], Medium Scale [500 kW - 5 MW], Large Scale [Above 5 MW]), By Application (Electricity Generation, Direct Use Combined Heat and Power [CHP], Vehicle Fuel), By End-User (Municipalities, Industrial Sector, Commercial Enterprises, Utilities), And By Region - Global Industry Insights, Overview, Comprehensive Analysis, Trends, Statistical Research, Market Intelligence, Historical Data and Forecast 2025 - 2034
Industry Insights
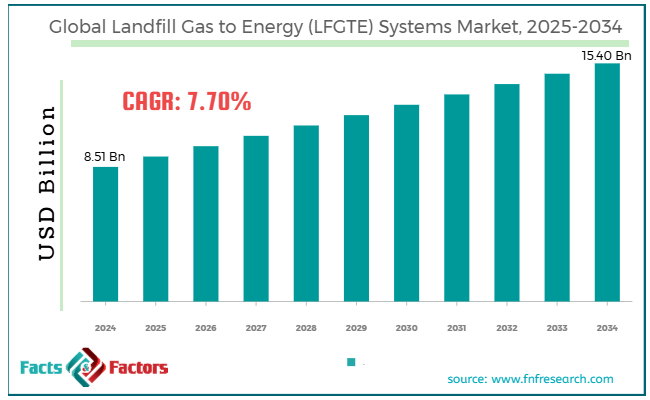
[221+ Pages Report] According to Facts & Factors, the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market size was worth around USD 8.51 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 15.40 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 7.70% between 2025 and 2034.
 Market Overview
Market Overview
Landfill gas-to-energy systems capture methane-rich gas formed by the natural decomposition of organic waste in landfills and convert it into usable energy. Rather than releasing this potent greenhouse gas into the atmosphere, the landfill gas-to-energy systems gather it via a series of pipes and wells and produce heat and electricity or upgrade it to natural gas (renewable). These systems offer a sustainable energy source, converting waste into a practical resource. The leading drivers of the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market are the growing emphasis on energy security and renewable energy, improvements in gas collection technologies, and surging demand for energy and elevated waste generation. The rising universal focus on renewable energy sources is a leading propeller for the market.
Organizations and governments prioritize substitute energy solutions to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and improve energy security. Landfill gas, a cost-effective and reliable fuel source, is gaining prominence for direct industrial and power production applications.
Also, technological improvements in purification and landfill gas collection are increasing the viability and efficiency of LFGTE systems. Developments in purification, gas extraction, and energy conversion solutions are improving methane capture rates and enhancing the superiority of recovered gas. Besides, the rising global energy demand and the need for clean energy sources fuel the need for LFGE plans.
Moreover, the need for effective waste management solutions, especially in crowded areas, is surging the need for LFGE as an ecological waste-to-energy option.
However, increasing competition from other renewable power solutions, policy uncertainty, and regulatory compliance costs could restrain the progress of the global market. The rising competitiveness of other renewable energy solutions, like wind and solar power, may offer challenges for LFGTE systems regarding investment allocation and market share.
Moreover, changes in regulations, government policies, and incentives may create risk and uncertainty for LFGTE project makers, thus hampering market growth. Nonetheless, the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems industry is expected to prosper due to opportunities such as integration with energy storage solutions and clean energy initiatives, as well as sustainability goals.
With advancements in energy storage solutions and smart grids, LFGTE systems are integrated more competently into the energy systems. This enables better energy reliability, load balancing, and enhanced use of landfill gas during high-demand times. Also, with the rising focus on achieving carbon neutrality, these systems will play a vital role in sustainable development.
 Key Insights:
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 7.70% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market size was valued at around USD 8.51 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 15.40 billion by 2034.
- The landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market is projected to grow significantly owing to strict environmental regulations, rising emphasis on energy security and renewable energy, and improvements in purification technologies.
- Based on capacity, the large scale (above 5 MW) segment is expected to lead the market, while the medium scale (500 kW - 5 MW) segment is expected to grow considerably.
- Based on application, the electricity generation segment is the dominating segment among others. In contrast, the combined heat and power (CHP) segment is projected to witness sizeable revenue over the forecast period.
- Based on end-user, the industrial sector segment is expected to lead the market as compared to the utilities segment.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
 Growth Drivers
Growth Drivers
- Will the mounting demand for clean energy and renewable sources drive the landfill gas to energy system industry growth?
The rising demand for clean and renewable energy sources is projected to fuel the growth of the landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market. The demand for ecological energy solutions is growing due to environmental issues, government policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and technological improvements. These systems effectively capture methane from landfills and transform it into viable energy, positively impacting cleaner energy generation.
- The growing investments in waste-to-energy projects considerably fuel the market growth
The rising investments in waste-to-energy plans are adding to the industry's growth. Private entities, governments, and environmental organizations are distributing funds to introduce more sustainable waste management technologies that comply with circular economy values.
In addition, the growing corporate commitment to carbon neutrality and sustainability motivates industries to capitalize on landfill gas recovery plans as a part of their ecological responsibility programs.
 Restraints
Restraints
- Does inconsistency in landfill gas generation rates and composition negatively impact the landfill gas to energy system market progress?
The quality and quantity of landfill gas can vary significantly due to the composition and age of the landfill, environmental conditions, and seasonal variations. This fluctuation offers challenges in maintaining operational efficiency and reliable energy production.
For instance, old landfills may generate smaller quantities of gas, while new ones may have high concentrations of methane but need complicated gas extraction solutions. These variations may result in periods of underperformance, impacting the economic practicality and complicating the design and planning of such solutions.
 Opportunities
Opportunities
- Are enhancements in gas conversion and capture positively impacting the landfill gas to energy system market growth?
Recent technological advancements have notably enhanced the cost-effectiveness and efficacy of landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems. Improvements in gas collection techniques, like enhanced monitoring systems and horizontal drilling, have improved the rates of methane capture.
Furthermore, enhancements in energy conversion and gas purification solutions allow the generation of high-quality RNG and energy. These advancements increase the prominence of LFGTE systems for operators and investors, thus expanding their use at different sites. The advancements ultimately fuel the progress of the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems industry.
 Challenges
Challenges
- Environmental and health issues restrict the growth of the market
Although landfill gas-to-energy (LFGTE) systems aim to mitigate methane releases, the combustion of landfill gas can generate pollutants such as carbon monoxide, dioxins, and nitrogen oxides. These harmful releases may adversely affect health and the environment, increasing concerns among the public and groups.
Moreover, the existence of toxic pollutants in landfill gas demands enhanced treatment and filtration solutions, which may negatively impact operational efficacy and increase prices.
 Report Scope
Report Scope
Report Attribute |
Details |
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 8.51 Billion |
Projected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 15.40 Billion |
CAGR Growth Rate |
7.70% CAGR |
Base Year |
2024 |
Forecast Years |
2025-2034 |
Key Market Players |
Waste Management Inc., Veolia, Republic Services Inc., Suez, Infinis Energy, Energy Developments Ltd (EDL), Clarke Energy, Aria Energy, DTE Vantage, Montauk Renewables, Fortistar, Siemens Energy, GE Vernova (formerly GE Power), Enerflex Ltd., Kohler Power Systems, and others. |
Key Segment |
By Capacity, By Application, By End-User, and Region |
Major Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East &, Africa |
Purchase Options |
Request customized purchase options to meet your research needs. Explore purchase options |
 Segmentation Analysis
Segmentation Analysis
The global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market is segmented based on capacity, application, end-user, and region.
Based on capacity, the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems industry is divided into small scale (below 500 kW), medium scale (500 kW - 5 MW), and large scale (above 5 MW). The large scale (above 5 MW) segment registered a larger market share in 2024 and will continue to dominate. This is due to the increasing emphasis on utilizing large landfill capacity for energy generation, as these sites typically produce substantial quantities of landfill gas. Large landfill gas-to-energy systems achieve high economies of scale, enhancing their cost-effectiveness and making them more appealing to landfill operators who can capitalize on them.
Based on the application, the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems industry is segmented into electricity generation, direct use, combined heat and power (CHP), and vehicle fuel. The electricity generation category is projected to capture a larger market share in the coming years. This technique utilizes landfill gas to power generators, engines, and turbines, generating electricity that can be sold or consumed on-site. The broad adoption of this application is fueled by its developed technology, financial viability, and favorable regulatory policies.
Based on end-user, the global market is segmented into municipalities, industrial sector, commercial enterprises, and utilities. The industrial sector is the leading segment in the market. It comprises chemical processing, manufacturing, and food production, with abundant on-site energy needs. Using landfill gas for fuel or electricity offers a cost-effective source to these facilities, reducing ecological impact and improving energy security.
 Regional Analysis
Regional Analysis
- What factors will help North America witness significant growth in the landfill gas to energy system market over the forecast period?
North America leads the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market in terms of a higher revenue share. The regional growth is attributed to favorable systems, technological improvements, regulatory support, and strong industry demand. The United States EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) and state-level RPS (Renewable Portfolio Standards) require utilities to produce a share of their electricity from renewable sources like landfill gas.
Companies in the region have introduced advanced technologies for landfill gas capture and utilization, including purification processes, gas collection systems, and power generation systems. Incorporating IoT and data analytics offers predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and improving operational efficacy in gas extraction.
Europe is expected to progress considerably, with a leading industry share after North America, backed by policy frameworks, innovations in gas extraction technologies, and strategic partnerships and investments. The European Union has set renewable energy goals, integrating landfill gas as a vital component in its renewable energy strategy. Economies like the United Kingdom and Germany have adopted policies that promote the utilization and recovery of landfill gas, obeying the widespread environmental objectives.
Modernizations in purification and gas extraction technologies have improved the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of landfill gas-to-energy (LFGTE) systems. Companies like Shell are capitalizing on biomethane generation with plans to construct plants in Germany. This will contribute to the nation’s consumption of biomethane, ultimately impacting the growth of the landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market.
Additionally, partnerships between private entities and governments have facilitated the expansion and development of landfill gas-to-energy projects in the region, thereby influencing regional growth.
 Competitive Analysis
Competitive Analysis
The key players profiled in the global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market include:
- Waste Management Inc.
- Veolia
- Republic Services Inc.
- Suez
- Infinis Energy
- Energy Developments Ltd (EDL)
- Clarke Energy
- Aria Energy
- DTE Vantage
- Montauk Renewables
- Fortistar
- Siemens Energy
- GE Vernova (formerly GE Power)
- Enerflex Ltd.
- Kohler Power Systems
 Key Market Trends
Key Market Trends
- Growth of hybrid waste-to-energy solutions:
Innovative hybrid systems blend different waste-to-energy solutions to reduce emissions and improve efficiency. These include mechanical conversion and biological processing that impact the overall industry progress.
- The growing integration of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
Projects like Norway’s Northern Lights initiative are discovering the incorporation of CCS with landfill gas to energy systems. By capturing carbon dioxide emissions from waste burning and storing them underground, these plans aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly, destroying nearly 400 million tons of carbon dioxide by 2050.
The global landfill gas to energy (LFGTE) systems market is segmented as follows:
 By Capacity Segment Analysis
By Capacity Segment Analysis
- Small Scale (Below 500 kW)
- Medium Scale (500 kW - 5 MW)
- Large Scale (Above 5 MW)
 By Application Segment Analysis
By Application Segment Analysis
- Electricity Generation
- Direct Use
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
- Vehicle Fuel
 By End-User Segment Analysis
By End-User Segment Analysis
- Municipalities
- Industrial Sector
- Commercial Enterprises
- Utilities
 By Regional Segment Analysis
By Regional Segment Analysis
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- The Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Egypt
- Kuwait
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Industry Major Market Players
- Waste Management Inc.
- Veolia
- Republic Services Inc.
- Suez
- Infinis Energy
- Energy Developments Ltd (EDL)
- Clarke Energy
- Aria Energy
- DTE Vantage
- Montauk Renewables
- Fortistar
- Siemens Energy
- GE Vernova (formerly GE Power)
- Enerflex Ltd.
- Kohler Power Systems
Frequently Asked Questions

Copyright © 2025 - 2026, All Rights Reserved, Facts and Factors


