Search Market Research Report
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Size, Share Global Analysis Report, 2025 - 2034
Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis Report By Type (Parabolic Trough Systems, Power Tower Systems, Dish/Engine Systems, and Others), By Application (Power Generation, District Heating and Cooling, Process Heating and Cooling), And By Region - Global Industry Insights, Overview, Comprehensive Analysis, Trends, Statistical Research, Market Intelligence, Historical Data and Forecast 2025 - 2034
Industry Insights
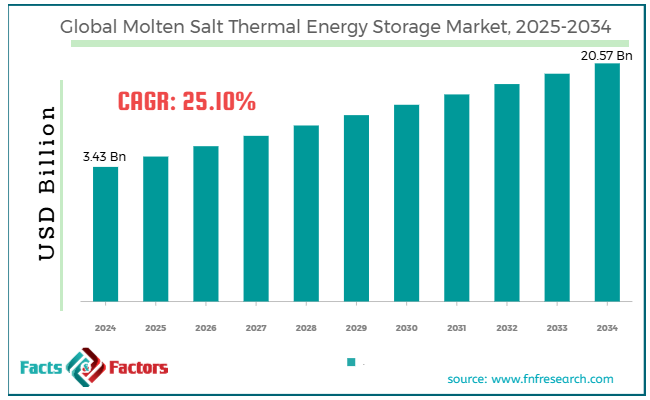
[221+ Pages Report] According to Facts & Factors, the global molten salt thermal energy storage market size was worth around USD 3.43 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 20.57 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 25.10% between 2025 and 2034.
 Market Overview
Market Overview
Molten salt (TES) thermal energy storage is a technology that stores heat for future use, generally in concentrated solar power (CSP) plants. It comprises heating a combination of salts, usually potassium nitrate and sodium nitrate, to high temperatures (typically 290°C -565°C), where molten salt retains thermal energy for many days. The worldwide molten salt thermal energy storage market is expected to grow substantially over the coming five years, owing to amplified deployment of renewable energy, increasing demand for grid stability, and enhancements in CSP (concentrated solar power). The universal shift towards renewable energy sources, especially solar power, has surged the demand for effective energy storage technologies. When integrated with CSP plants, molten salt thermal energy storage systems offer a trustworthy solution to store and supply solar energy during peak periods.
With the growing prevalence of wind and solar renewable energy sources, the maintenance of grid stability becomes difficult because of their intermittent nature. MSTES solves this challenge by storing surplus energy and releasing it during sunny days, promising a constant energy supply.
Moreover, improvements in CSP solutions, comprising highly efficient heat exchanges and enhanced heat transfer fluids, improved the performance of molten salt thermal energy storage systems, increasing their efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
However, a few factors hampering the molten salt thermal energy storage industry’s growth include low technological sophistication and cold climate restrictions. Since MSTES technology is highly efficient, it still lacks further development. Challenges, such as corrosion, material degradation, and efficacy optimization, have yet to be addressed to improve system performance and reliability.
Moreover, the molten salts used in MSTES systems require high freezing points, which limits their efficiency in cold climates. This raises the demand for extra heating mechanisms or the development of novel salt preparations with minimal freezing points. Nonetheless, the global market will gain notable progress backed by the development of molten salts with low freezing points and incorporation with hybrid energy systems.
Growing research in salt combinations that stay liquid at low temperatures may extend the applications of MSTES to cold places and allow seasonal power storage. In addition, amalgamating MSTES with other energy storage solutions may offer a comprehensive solution that leverages the strengths of every system, improving overall reliability and efficacy.
 Key Insights:
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global molten salt thermal energy storage market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 25.10% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global molten salt thermal energy storage market size was valued at around USD 3.43 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 20.57 billion by 2034.
- The molten salt thermal energy storage market is projected to grow significantly owing to the amplified deployment of renewable energy, increasing demand for grid reliability, and supportive government policies for thermal storage.
- Based on type, the parabolic trough systems segment is expected to lead the market, while the power tower systems segment is expected to grow considerably.
- Based on the application, the power generation segment is expected to lead the market compared to the district heating and cooling segment.
- Based on region, Europe is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by North America.
 Growth Drivers
Growth Drivers
- How are the growing commercial and industrial applications triggering the growth of the molten salt thermal energy storage market?
Apart from renewable energy generation, molten salt thermal energy storage is gaining attraction and significance in commercial and industrial applications. Industries that need high-temperature process heat, like chemical processing, steel production, and cement manufacturing, are discovering molten salt thermal energy storage as a clean substitute for fossil fuel-powered heating. Molten salts can effectively store thermal energy at 550°C or higher, enhancing their suitability for industrial applications requiring high-temperature heating.
Moreover, several industries are under pressure to decarbonize and lessen their carbon emissions. Molten salt thermal energy storage is a clean substitute for coal or natural gas in heating systems. It aids these industries in meeting ecological rules.
Denmark's Hyme Energy molten hydrozide salt energy storage project (2024) is the best example of extending MSTES into industrial uses. This project emphasizes process heat storage and demonstrates how MSTES can be utilized in addition to conventional solar power plants.
- Advancements in molten salt technology will noticeably impact market growth
Technological improvements in storage system designs and molten salt preparations have been vital in enhancing the performance of molten salt thermal energy storage systems. In the past decade, major research has emphasized enhancing molten salt systems' thermal efficacy, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Conventional molten salts have high freezing points, which may restrict their operations in cold places.
Nonetheless, growing research in low-freezing-point salts has streamlined the MSTES systems to perform at low temperatures, thus increasing their applicability. In addition, improvements in heat transfer fluids and heat exchangers have enhanced the efficiency of storing and releasing thermal energy in these solutions, thus increasing their feasibility for large-scale use. All these prospects add to the global progress of the molten salt thermal energy storage industry.
 Restraints
Restraints
- Will the environmental and safety concerns negatively impact the molten salt thermal energy storage market progress?
The functioning of MSTES systems comprises storing and handling high-temperature molten salts, which may offer safety risks if not correctly managed. The capability of spills or leaks of molten salts, which are mostly corrosive, may result in ecological contamination.
Moreover, using molten salts may pose environmental issues since inadequate disposal may contaminate water and soil. These ecological and safety issues demand strict hazard alleviation measures and safety protocols, contributing to the operational complexity and prices of molten salt thermal energy storage systems.
 Opportunities
Opportunities
- How is the growth of advanced low-freezing-point molten salts positively impacting the molten salt thermal energy storage market growth?
One of the promising enhancements in the molten salt thermal energy storage market is the development of advanced molten salts that remain liquid at the lowest temperatures. Conventional molten salts, like a blend of potassium nitrate and sodium nitrate, have comparatively high freezing points, which restrict their operative range, mainly in cold climates with seasonal temperature fluctuations.
However, research has produced novel molten salt formulations that are fluid at low temperatures. These modernizations are increasing the potential of molten salt thermal energy storage systems to be utilized in cold places where conventional molten salts might freeze. Besides, they can also allow seasonal thermal energy storage.
 Challenges
Challenges
- High competition from other energy storage technologies restricts the growth of the market
MSTES faces intense competition from other energy storage solutions, such as pumped hydro storage and lithium-ion batteries, which primarily reduce costs and complicate installation. Enhancements in battery solutions have resulted in advancements in energy efficiency and density, thus increasing their appeal to potential investors. The established systems and broad adoption of these solutions complicate the industry ranking of molten salt thermal energy storage systems.
 Report Scope
Report Scope
Report Attribute |
Details |
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 3.43 Billion |
Projected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 20.57 Billion |
CAGR Growth Rate |
25.10% CAGR |
Base Year |
2024 |
Forecast Years |
2025-2034 |
Key Market Players |
Yara International ASA, Acciona S.A., Abengoa Solar S.A., BrightSource Energy Inc., SENER Grupo de Ingeniería S.A., SolarReserve LLC, ENGIE SA, SCHOTT AG, Siemens Energy AG, Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne Inc., Wilson Solarpower, ESolar, EnergyNest AS, MoltexFLEX Ltd., Copenhagen Atomics, and others. |
Key Segment |
By Type, By Application, and Region |
Major Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East &, Africa |
Purchase Options |
Request customized purchase options to meet your research needs. Explore purchase options |
 Segmentation Analysis
Segmentation Analysis
- The global molten salt thermal energy storage market is segmented based on type, application, and region.
Based on type, the global molten salt thermal energy storage industry is divided into parabolic trough systems, power tower systems, dish/engine systems, and others. The parabolic trough systems segment held the maximum market share in the previous years and is expected to dominate due to its scalability, proven cost-effectiveness, and technology.
The present research on enhancing efficiency and materials is expected to improve its competitiveness further. They use parabolic-shaped mirrors to focus sunshine onto a receiver tube, where molten salt stores and absorbs the thermal energy. This technology has been developed and adopted in many large-scale projects on a global scale.
Based on the application, the global molten salt thermal energy storage industry is segmented into power generation, district heating and cooling, and process heating and cooling. The power generation segment registered a larger market share, accounting for nearly 60% of the global industry share in 2024. As a thermal energy storage medium and heat transfer fluid, molten salt is widely used in CSP plants. The benefits include a dispatchable energy supply and improved efficiency.
Molten salt systems allow CSP plants to produce energy even when sunlight is unavailable, offering a reliable and stable energy supply. The high thermal capacity of these salts enables effective heat retrieval and storage, thus enhancing the overall functioning of energy generation systems.
 Regional Analysis
Regional Analysis
- What factors will help Europe to witness significant growth in the molten salt thermal energy storage market?
Europe has held a leading share of the molten salt thermal energy storage market in the past few years and is expected to continue progressing remarkably over the estimated period. The key propellers to regional growth comprise climate commitment and policy support, industry leadership, well-developed infrastructure, and excellence in R&D activities. Europe enforced determined climate objectives like net-zero emissions by 2050, which majorly fueled investments in renewable energy solutions. MSTES systems are vital to these initiatives, supporting the incorporation of renewable energy sources into the grid.
Nations like Italy, Germany, and Spain have been leaders in deploying CSP plants that use molten salt storage. Europe also brags about its developed MSTES systems, with several CSP plants embedded with MSTES. The prominent projects comprise Andasol Solar Power Station and Gemasolar in Spain.
In addition, the region is home to a substantial research and development infrastructure emphasizing MSTES solutions. Key initiatives include Horizon Europe's back modernization in thermal energy storage that supports system efficiencies and materials improvements. Collaborations among industry leaders, academic institutions, and government bodies have marked Europe as a key center for innovations in molten salt thermal energy storage.
North America holds a second-leading share in the worldwide molten salt thermal energy storage market, backed by strong R&D infrastructure, strategic industry associations, and a supportive policy environment. North America brags about its developed R&D infrastructure, represented by institutions such as Sandia National Laboratories. These institutions are essential in enhancing MSTES technologies through the modernization of materials and systems performance.
North American firms like SolarReserve and BrightSource Energy have joined hands to develop and arrange MSTES systems. Associations with international stakeholders and companies have supported the scaling up of molten salt thermal energy storage solutions, which improve energy reliability and grid stability.
Moreover, the United States federal government has adopted different policies to encourage the use of renewable energy, including grants and tax incentives for MSTES projects. State-level programs like RPS (Renewable Portfolio Standards) further incentivize the incorporation of thermal energy storage technologies with renewable sources.
 Competitive Analysis
Competitive Analysis
The global molten salt thermal energy storage market lead the Players like:
- Yara International ASA
- Acciona S.A.
- Abengoa Solar S.A.
- BrightSource Energy Inc.
- SENER Grupo de Ingeniería S.A.
- SolarReserve LLC
- ENGIE SA
- SCHOTT AG
- Siemens Energy AG
- Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne Inc.
- Wilson Solarpower
- ESolar
- EnergyNest AS
- MoltexFLEX Ltd.
- Copenhagen Atomics
 Key Market Trends
Key Market Trends
- Surging demand for durable energy storage:
With the rise of intermittent renewables, molten salt thermal energy storage is gaining prominence as a long-duration and cost-effective solution that outshines batteries in many high-temperature and large-scale applications.
- Cost reduction and technological innovation:
The present research and development in molten salt blends, more efficient heat exchanges, and enhanced corrosion resistance are aiding the progress of down CAPEX and improving system efficiency and lifespan.
The global molten salt thermal energy storage market is segmented as follows:
 By Type Segment Analysis
By Type Segment Analysis
- Parabolic Trough Systems
- Power Tower Systems
- Dish/Engine Systems
- Others
 By Application Segment Analysis
By Application Segment Analysis
- Power Generation
- District Heating and Cooling
- Process Heating and Cooling
 By Regional Segment Analysis
By Regional Segment Analysis
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- The Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Egypt
- Kuwait
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Industry Major Market Players
- Yara International ASA
- Acciona S.A.
- Abengoa Solar S.A.
- BrightSource Energy Inc.
- SENER Grupo de Ingeniería S.A.
- SolarReserve LLC
- ENGIE SA
- SCHOTT AG
- Siemens Energy AG
- Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne Inc.
- Wilson Solarpower
- ESolar
- EnergyNest AS
- MoltexFLEX Ltd.
- Copenhagen Atomics

Copyright © 2025 - 2026, All Rights Reserved, Facts and Factors


