Search Market Research Report
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (IPSC) Market Size, Share Global Analysis Report, 2025 – 2034
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (IPSC) Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis Report By Derived Cell Type (Hepatocytes, Fibroblasts, Keratinocytes, Amniotic Cells, Others), By Application (Drug Development, Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine, Toxicology Research, Disease Modeling), By End-Use (Academic & Research Institutes, Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, and Others), And By Region - Global Industry Insights, Overview, Comprehensive Analysis, Trends, Statistical Research, Market Intelligence, Historical Data and Forecast 2025 – 2034
Industry Insights
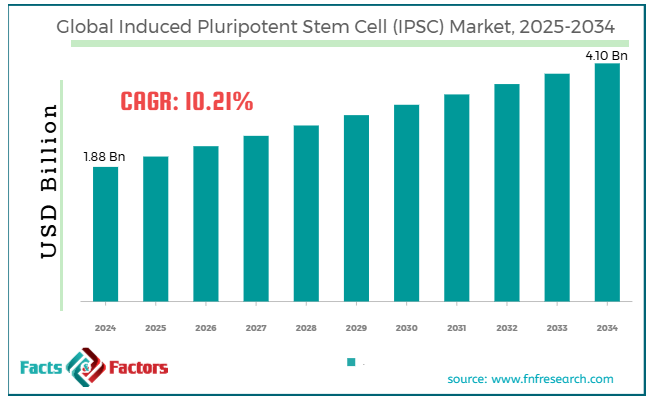
[221+ Pages Report] According to Facts & Factors, the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market size was worth around USD 1.88 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 4.10 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 10.21% between 2025 and 2034.
 Market Overview
Market Overview
Induced pluripotent stem cells are derived from the reprogramming of adult somatic cells, such as blood or skin cells, into a pluripotent state, allowing them to differentiate into any cell type in the body. This innovation enables the production of patient-specific stem cells without ethical issues. iPSCs are a prevailing tool offering potential treatment for a broader range of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
The primary driving factors of the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market include the rising demand for regenerative medicine, advancements in cellular reprogramming methods, and the increasing prevalence of neurological illnesses. The rising cases of chronic diseases and organ failure have increased interest in regenerative treatments. iPSCs offer patient-based treatment, reducing immune rejection. This trend is fueling the adoption of iPSC solutions in therapy development and clinical research.
Additionally, enhanced techniques for reprogramming somatic cells have improved the safety and efficiency of generating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Modernizations, such as CRISPR editing and non-integrating vectors, are minimizing the risks associated with gene modification. These improvements are appealing to investors and researchers in the domain.
Furthermore, neurological illnesses like Alzheimer's, ALS, and Parkinson's are complex to model with conventional techniques. iPSCs enable researchers to produce neural cells from individuals (patients) to understand disease mechanisms in vitro. This ability supports the development of targeted therapies, which in turn impact demand.
Nevertheless, the market progress is hampered by safety concerns on tumorigenicity and technical intricacies in reprogramming efficacy. iPSCs have a risk of creating tumors or teratomas if not completely differentiated before transplantation. This presents significant challenges for clinical applications in humans. Promising complete and safe cell differentiation is still a key challenge for the research groups.
Additionally, the conversion of somatic cells into iPSCs can be variable and inefficient among different cell types. Hence, low reprogramming may adversely impact reproducibility and scalability. This constrains the dependency of iPSCs for clinical and industrial applications.
Yet, the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) industry is expected to gain momentum over the coming years. Pharmaceutical companies are widely using iPSC-based cell lines to model illnesses and test drugs. This lessens dependency on animal testing and offers opportunities for iPSC providers.
Moreover, iPSC lines obtained from different cell banks help build global disease models and provide off-the-shelf solutions, thus increasing the demand for iPSC biobanking.
 Key Insights:
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 10.21% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market size was valued at around USD 1.88 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.10 billion by 2034.
- The induced pluripotent stem cell IPSC market is projected to grow significantly due to the mounting demand for regenerative medicine, the growth of personalized medicine, and supportive institutional and government funding.
- Based on the derived cell type, the hepatocytes segment is expected to lead the market, while the fibroblasts segment is expected to grow considerably.
- Based on application, the drug development is the largest segment, while the disease modeling segment is projected to witness a sizable revenue growth over the forecast period.
- Based on end-use, the pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies segment is expected to lead the market compared to the academic & research institutes segment.
- Based on region, North America is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by Europe.
 Growth Drivers
Growth Drivers
- Growing applications in toxicity testing and drug discovery boost market growth
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies are primarily using iPSCs for disease modeling, drug discovery, and toxicity testing, as they serve as a substitute for conventional animal models that often fail to predict human responses accurately. iPSC-based cells enable disease-specific and patient-specific testing, boosting drug development schedules and enhancing safety profiles.
The latest news from leading pharmaceutical companies has declared the meticulous use of iPSC-based cardiomyocytes to predict the cardiotoxicity of novel drug candidates, which has significantly reduced late-stage drug failures.
- Increasing funding and investments in regenerative medicine fuel the market growth
The global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market is primarily driven by rising government funding, partnerships between academic institutions and biotech companies, and private investments. Global governments are emphasizing regenerative medicine as a key component of their national health strategies due to its ability to address unmet medical needs.
Private sector involvement is also rising substantially. Leading pharmaceutical companies, such as Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics, Novartis, and Takeda, have recently increased their research and development spending on iPSC solutions.
 Restraints
Restraints
- Tumorigenicity risk and safety concerns unfavorably impact market progress
Safety issues remain a key barrier, particularly the risk of tumor formation following the transplantation of iPSC-based cells. Since iPSCs exhibit pluripotency, there is an increased risk of undifferentiated cells proliferating uncontrollably, potentially leading to the formation of teratomas or other types of tumors.
A clinical experiment using iPSC-based cardiac therapy was provisionally halted in early 2025 after detecting abnormal cell growth in a subset of patients. This underscored continuing safety issues and the demand for enhanced quality control.
 Opportunities
Opportunities
- Advancements enhancing scalability and efficiency positively impact market growth
Constant improvements in gene editing, such as CRISPR, automated cell culture systems, 3D bioprinting, and AI-based protocol optimization, offer crucial opportunities to overcome the present limitations of iPSC technology. This notably impacts the growth of the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) industry.
A biopharma giant and a prominent AI company announced a platform that combines robotics and machine learning in early 2025. It aimed to produce clinical-grade iPSC-based cells with 50 percent reduced contamination risk and enhanced efficacy.
 Challenges
Challenges
- Limited expertise and infrastructure restrict the growth of the market
iPSC manufacturing and research require a well-developed infrastructure that includes advanced imaging, GMP-compliant cell culture facilities, and genomic screening solutions. There is also a growing need for professional specialists in stem cell biology, regenerative medicine, and bioinformatics.
In 2024, a group of academic institutions introduced a dedicated training program to address the worldwide shortage of stem cell-producing experts. This underscored the current demand for capacity building.
 Report Scope
Report Scope
Report Attribute |
Details |
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 1.88 Billion |
Projected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 4.10 Billion |
CAGR Growth Rate |
10.21% CAGR |
Base Year |
2024 |
Forecast Years |
2025-2034 |
Key Market Players |
Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics Inc. (FCDI), Thermo Fisher Scientific, Takara Bio Inc., Lonza Group, STEMCELL Technologies Inc., Evotec SE, REPROCELL Inc., Pluricell Biotech, Bit Bio, BlueRock Therapeutics, Century Therapeutics, Axol Bioscience Ltd., Cellular Dynamics International, Novo Nordisk, Astellas Pharma, and others. |
Key Segment |
By Derived Cell Type, By Application, By End-Use, and Region |
Major Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East &, Africa |
Purchase Options |
Request customized purchase options to meet your research needs. Explore purchase options |
 Segmentation Analysis
Segmentation Analysis
The global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market is segmented based on derived cell type, application, end-use, and region.
Based on derived cell type, the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) industry is divided into hepatocytes, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, amniotic cells, and others. The hepatocytes segment registered a remarkable share of the market. Their potential to imitate the function of primary human liver cells increases their significance for hepatotoxicity testing, liver disease modeling, and drug metabolism. Pharmaceutical firms are primarily dependent on iPSC-based hepatocytes for preclinical screening, which helps reduce late-stage drug failures. They are also widely used in applications related to regenerative medicine and cell therapy for liver diseases. The amalgamation of functionality, scalability, and demand in numerous sectors fuels their industry prominence.
Based on application, the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market is segmented into drug development, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, toxicology research, and disease modeling. The drug development segment leads the global market in terms of revenue. iPSC cells offer relevant human models for metabolism, drug efficacy, and toxicity, which enhances preclinical prediction and lessens dependency on animal models. Pharmaceutical companies widely utilize iPSC platforms to identify potential candidate compounds and gain a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms. The potential to model patient-specific reactions also backs personalized drug development. As drug research and development budgets grow, the need for iPSC technologies also escalates.
Based on end-use, the global market is segmented into academic & research institutes, pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies, and others. The pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies segment dominates the worldwide market. These companies are key drivers of iPSC adoption due to their significant investments in the drug discovery domain, the development of regenerative therapies, and toxicology testing. Their emphasis on reducing late-stage failures and boosting drug development increases the value of iPSC technology. Moreover, biotech and pharmaceutical companies actively collaborate with iPSC technology providers to produce patient-specific disease models, thereby improving precision medicine methods.
 Regional Analysis
Regional Analysis
- North America to witness significant growth over the forecast period
North America held a dominant share of the worldwide induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market due to its strong research infrastructure, substantial funding, and the presence of prominent pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. North America brags about its well-developed universities, biotech hubs, and research hospitals that fuel innovations in iPSCs. These institutes offer improved labs and superior technologies vital for stem cell research. This infrastructure appeals to global investments and talent.
The region receives significant funding from governments, including the NIH, which allocates over USD 1.5 billion annually for stem cell research. Pharmaceutical R&D budgets and private venture capital strengthen financial backing. Thus, funding boosts the commercialization and discovery of iPSC products.
Furthermore, North America is led by several biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies actively advancing iPSC solutions. These companies invest heavily in personalized medicine and drug discovery using iPSCs. Their engagement fuels the adoption and industry growth.
The European induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) industry is progressing as the second-leading region, supported by a robust biomedical research network, a developing regulatory framework, and substantial EU and government funding. Europe boasts a well-developed ecosystem of leading research institutions dedicated to stem cell science. Companies like the European Stem Cell Network and EMBL foster collaboration and innovation. This robust network supports translational and basic iPSC research.
The European Medicines Agency provides balanced and clear protocols for ATMPs (Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products), such as iPSCs. This clarity in regulations streamlines market entry and clinical trial approvals, thus creating a favorable environment for patient safety and advancements.
Moreover, the EU and European governments capitalize on programs to advance regenerative medicine. This financial backing aids private-public partnerships and the development of iPSC technology. Constant funding boosts commercialization and research.
 Competitive Analysis
Competitive Analysis
The players profiled in the global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market include:
- Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics Inc. (FCDI)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Takara Bio Inc.
- Lonza Group
- STEMCELL Technologies Inc.
- Evotec SE
- REPROCELL Inc.
- Pluricell Biotech
- Bit Bio
- BlueRock Therapeutics
- Century Therapeutics
- Axol Bioscience Ltd.
- Cellular Dynamics International
- Novo Nordisk
- Astellas Pharma
 Key Market Trends
Key Market Trends
- Growth of AI-based and Automated cell culture:
Artificial intelligence and automation technologies are primarily adopted to simplify the differentiation process and iPSC culture. Automated systems reduce human error, scale up production, and enhance reproducibility, while artificial intelligence algorithms predict cell behavior and refine differentiation protocols. This boosts iPSC production, making it more cost-effective and highly consistent.
- The advent of universal donor iPSC lines:
Scientists are developing 'universal donor' or hypoimmunogenic induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines through gene editing to minimize the risks of immune rejection. These lines can be used for allogeneic therapies, notably reducing production times and costs compared to patient-specific methods, thereby expanding therapeutic potential and strengthening clinical adoption.
The global induced pluripotent stem cell (IPSC) market is segmented as follows:
 By Derived Cell Type Segment Analysis
By Derived Cell Type Segment Analysis
- Hepatocytes
- Fibroblasts
- Keratinocytes
- Amniotic Cells
- Others
 By Application Segment Analysis
By Application Segment Analysis
- Drug Development
- Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine
- Toxicology Research
- Disease Modeling
 By End-Use Segment Analysis
By End-Use Segment Analysis
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Others
 By Regional Segment Analysis
By Regional Segment Analysis
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- The Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Egypt
- Kuwait
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Industry Major Market Players
- Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics Inc. (FCDI)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Takara Bio Inc.
- Lonza Group
- STEMCELL Technologies Inc.
- Evotec SE
- REPROCELL Inc.
- Pluricell Biotech
- Bit Bio
- BlueRock Therapeutics
- Century Therapeutics
- Axol Bioscience Ltd.
- Cellular Dynamics International
- Novo Nordisk
- Astellas Pharma
Frequently Asked Questions

Copyright © 2025 - 2026, All Rights Reserved, Facts and Factors


